Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to long-term investing, one of the most powerful concepts you can apply is Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT). Developed by Harry Markowitz, MPT helps investors minimize risk and maximize returns through diversification. But what exactly is diversification, and how does it work in practice? In this blog, we’ll break down MPT in simple terms and explain how diversification can help protect your investments.
What is Modern Portfolio Theory?
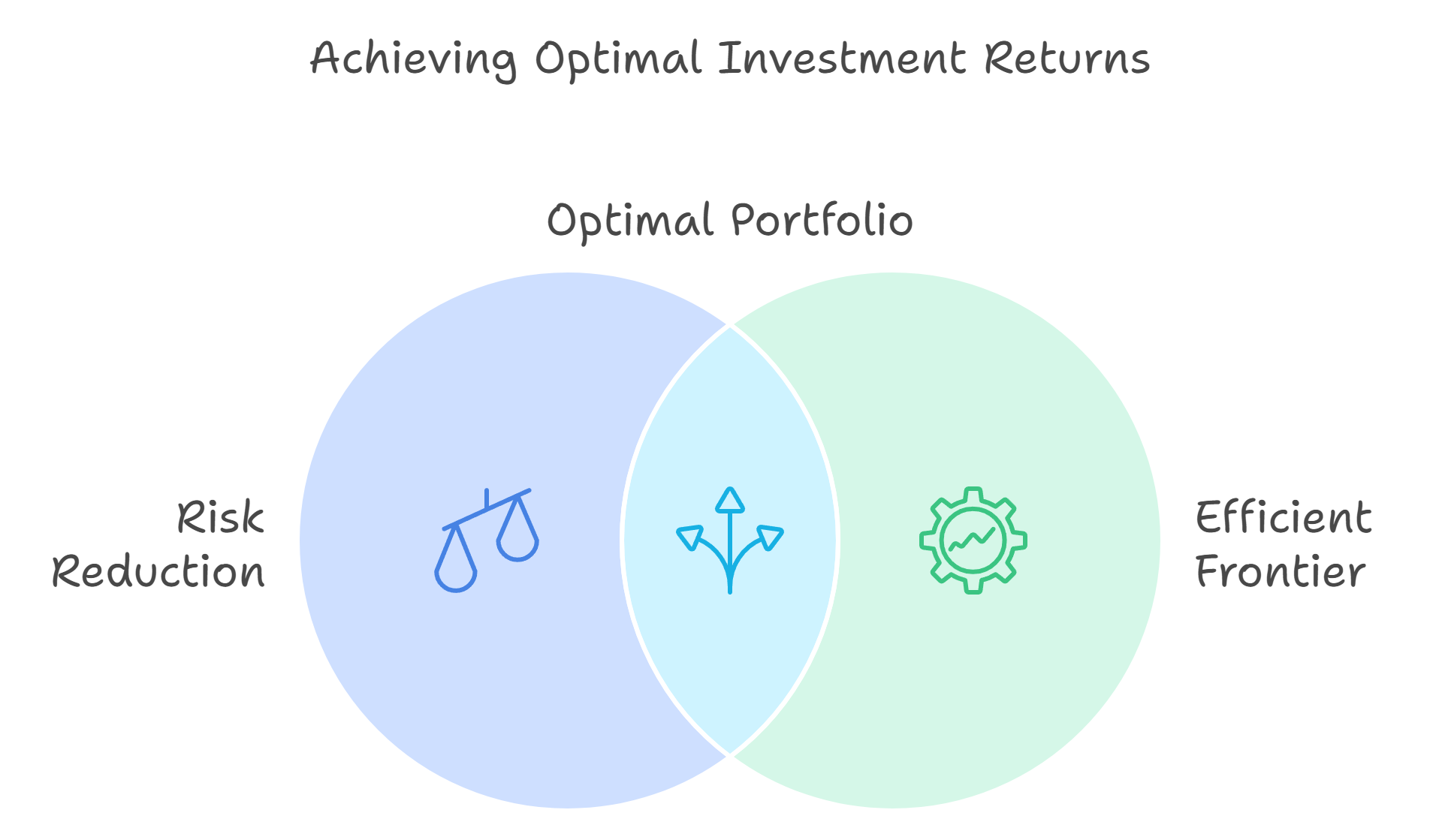
Modern Portfolio Theory is based on the idea that investors can build an “efficient portfolio” that maximizes returns for a given level of risk. The core principle of MPT is diversification, which means spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce the overall risk.
- Risk Reduction: MPT shows that by investing in assets that don’t move in the same direction at the same time, you can lower your overall risk. For example, stocks and bonds often behave differently—when stock prices fall, bond prices may rise, helping to balance out losses.
- Efficient Frontier: MPT introduces the concept of the efficient frontier, which is a set of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a defined level of risk. The goal is to be on the efficient frontier, where you’re getting the best possible return for the amount of risk you’re taking.
The Basics of Diversification
Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across different assets, sectors, or regions to reduce risk. Here’s how diversification works:
- Asset Classes: Diversify across different types of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. Each asset class has different risk and return characteristics, which helps reduce the overall volatility of your portfolio.
- Sectors and Industries: Within the stock market, diversify across different sectors (e.g., technology, healthcare, finance). This way, if one sector underperforms, others may compensate for the losses.
- Geographical Diversification: Investing in both domestic and international markets helps protect your portfolio from regional economic downturns.
Everyday Example: Imagine you’re making a fruit salad. If you only use apples and they spoil, the entire salad is ruined. But if you use apples, bananas, and berries, and one fruit spoils, you still have a good salad. Diversification works similarly by reducing the impact of any one poor investment.
Why Diversification Matters
Diversification is important because it helps:
- Reduce Volatility: By holding different types of investments, you can minimize the impact of any single asset’s poor performance.
- Protect Against Downside Risk: Not all assets will perform poorly at the same time. Diversification ensures that losses in one area can be offset by gains in another.
- Achieve More Stable Returns: A diversified portfolio tends to have smoother, more stable returns over the long term, making it easier to stay invested during market fluctuations.
Modern Portfolio Theory and the concept of diversification are foundational for long-term investors. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and regions, you can lower your overall risk while increasing the potential for stable returns. Diversification is a powerful way to achieve long-term investing success without exposing yourself to unnecessary risks.