Table of Contents
Introduction
If you’ve ever dreamed of owning property and watching its value grow over time, then real estate investing might be the right path for you. Real estate is one of the oldest and most reliable investment methods, offering a mix of steady income, property appreciation, and diversification. But how does it work? Is it really as simple as buying a house and waiting for it to gain value? In this guide, we’ll introduce you to the basics of real estate investing and help you understand what makes it such an attractive option for building wealth.
Why Consider Real Estate as an Investment?
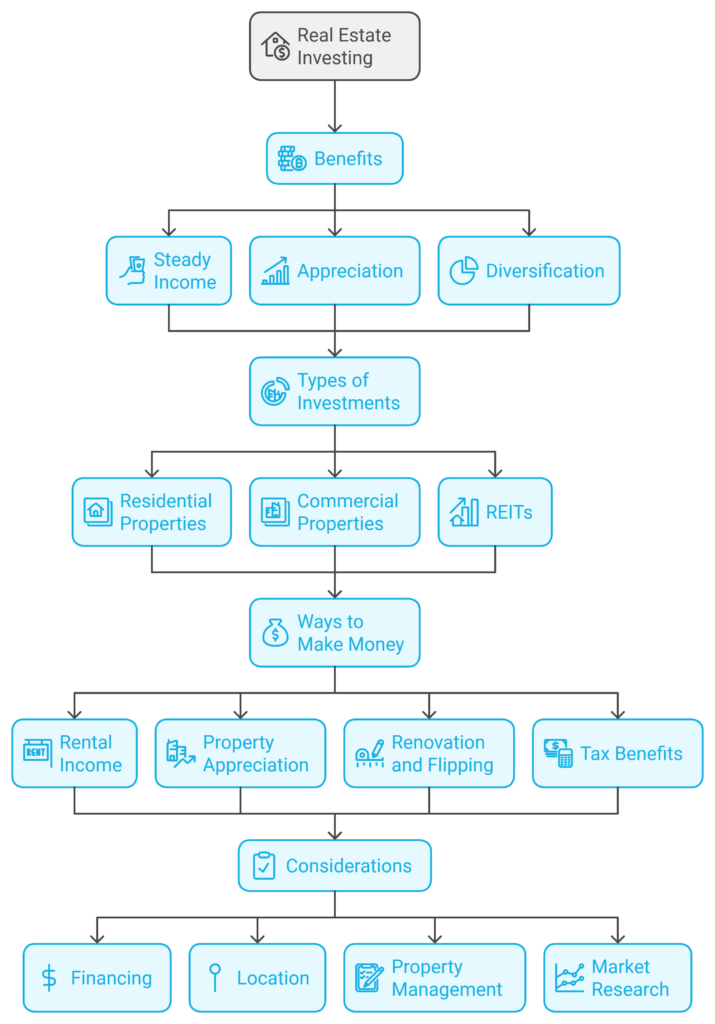
Real estate offers a unique set of benefits that make it an attractive option for many investors. Here are some of the main reasons why people choose to invest in real estate:
- Steady Income:
One of the most appealing aspects of real estate is the potential for rental income. When you own a rental property, you can earn money every month from tenants who pay to live or work there. This creates a steady stream of passive income that can be a great supplement to your regular job. - Appreciation:
Appreciation is the increase in property value over time. Historically, real estate tends to appreciate, especially in desirable locations. This means that not only are you earning rental income, but your property itself could be gaining value. - Diversification:
Real estate is a great way to diversify your investment portfolio. Unlike stocks or bonds, real estate values aren’t directly tied to the performance of financial markets, so they can help balance your overall risk.
Example:
If you bought a small rental property for $200,000 and held it for ten years, the property value might increase to $300,000 due to market appreciation. During this time, you also collected rent from tenants, giving you an additional income stream.
Types of Real Estate Investments
There’s more to real estate investing than just buying and renting out a house. Here are some common types of real estate investments you can consider:
- 1. Residential Properties:
This includes single-family homes, multi-family units, condominiums, and apartments. Investors can rent these properties out to tenants and collect rental income. Residential properties are often a good starting point for beginners. - 2. Commercial Properties:
These are properties used for business purposes, such as office buildings, retail spaces, or warehouses. Commercial real estate typically offers higher returns compared to residential but also comes with higher risks and costs. - 3. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
If you want to invest in real estate without buying a physical property, REITs are a good option. REITs are companies that own, operate, or finance real estate that produces income. When you invest in a REIT, you’re buying shares in that company, similar to buying shares of a stock. This is a way to invest in real estate passively and get access to larger commercial properties.
Example:
If you want to invest in real estate but don’t want to deal with tenants or property maintenance, you could invest in a REIT. You would get the benefits of real estate investment, like income from rent, without the hassles of managing physical property.
How to Make Money from Real Estate
There are several ways to make money from real estate investing:
- 1. Rental Income:
When you buy a rental property, tenants pay you rent each month. After covering expenses like mortgage payments, property taxes, and maintenance, you keep the remaining profit. Over time, rental income can become a steady source of passive cash flow. - 2. Property Appreciation:
Real estate often increases in value over time. If you hold a property for several years, you may be able to sell it for much more than you originally paid, realizing a significant capital gain. - 3. Renovation and Flipping:
Some investors make money by buying properties, renovating them, and selling them at a higher price. This is known as house flipping. It requires good knowledge of the market and renovation costs, but it can be highly profitable when done correctly.
Example:
Jane buys an old house for $150,000, spends $30,000 on renovations, and sells it for $220,000. After expenses, she earns a profit of $40,000.
- 4. Tax Benefits:
Real estate investors enjoy tax deductions on mortgage interest, property taxes, operating expenses, depreciation, and repairs. These tax benefits can help reduce the overall cost of investing and increase net returns.
Key Considerations Before Investing in Real Estate
Investing in real estate isn’t as straightforward as it may seem. Here are some important factors to consider:
- 1. Financing:
Most real estate investors use mortgages to purchase properties. This means taking on debt, so it’s crucial to have a solid financial plan to cover mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and other costs. It’s important to shop around for a good mortgage rate to keep your costs as low as possible. - 2. Location, Location, Location:
The location of a property is one of the biggest factors affecting its value. Properties in good locations — near schools, parks, amenities, and with good public transport, will generally be more desirable, leading to higher rental income and appreciation. - 3. Property Management:
If you own rental properties, you need to manage them, finding tenants, maintaining the property, handling repairs, and more. Some investors hire property management companies to handle these tasks, but that also means additional costs. - 4. Market Research:
Knowing the local market is key to a successful investment. Are property values in the area rising? Is there demand for rental properties? Understanding these factors will help you make smarter investment decisions.
Example:
Tom wants to invest in a rental property. He looks for a property near a university because he knows there’s consistent demand from students needing housing. This reduces the risk of having an empty property with no rental income.
Pros and Cons of Real Estate Investing
Like any investment, real estate comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Steady Cash Flow: Rental properties can provide a stable income stream.
- Tax Benefits: Investors can write off expenses such as property taxes, mortgage interest, and depreciation.
- Tangible Asset: Unlike stocks or bonds, real estate is a physical, tangible asset that you can see and use.
Cons:
- Requires Capital: Buying real estate often requires a substantial upfront investment, either in cash or through financing.
- Illiquidity: Real estate isn’t as easy to sell as stocks or bonds. It may take months to find a buyer, which means your money is tied up for a while.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Properties need upkeep, and being a landlord comes with responsibilities like property repairs and dealing with tenants.
Real estate is an attractive investment option for building wealth, offering steady income, property appreciation, and tax benefits. However, it’s also a commitment that requires careful planning, market research, and a solid financial strategy. Whether you’re interested in rental properties, commercial spaces, or REITs, understanding the basics of real estate will help you make informed investment decisions.
Want to learn more about how real estate fits into a well-diversified investment strategy? Use ValueIt to explore how to balance your portfolio and maximize long-term returns. With the right knowledge and tools, real estate can be a rewarding part of your wealth-building journey.